The HOMFLY-PT Polynomial: Difference between revisions
DrorsRobot (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Manual TOC Sidebar}} |
{{Manual TOC Sidebar}} |
||
The ''HOMFLY-PT polynomial'' <math>H(L)(a,z)</math> (see {{ref|HOMFLY}} and {{ref|PT}} of a knot or link <math>L</math> is defined by the skein relation |
The ''HOMFLY-PT polynomial'' <math>H(L)(a,z)</math> (see {{ref|HOMFLY}} and {{ref|PT}}) of a knot or link <math>L</math> is defined by the skein relation |
||
<center><math> |
<center><math> |
||
aH\left(\ |
aH\left(\overcrossing\right)-a^{-1}H\left(\undercrossing\right)=zH\left(\smoothing\right) |
||
-a^{-1}H\left(\{undercrossing\}\right) |
|||
= zH\left(\{smoothing\}\right) |
|||
</math></center> |
</math></center> |
||
and by the initial condition <math>H(\ |
and by the initial condition <math>H(\bigcirc)</math>=1. |
||
<code>KnotTheory`</code> knows about the HOMFLY-PT polynomial: |
<code>KnotTheory`</code> knows about the HOMFLY-PT polynomial: |
||
| Line 15: | Line 13: | ||
{{Startup Note}} |
{{Startup Note}} |
||
<!--$$?HOMFLYPT$$--> |
<!--$$?HOMFLYPT$$--> |
||
<!--Robot Land, no human edits to "END"--> |
|||
<!--The lines to END were generated by WikiSplice: do not edit; see manual.--> |
|||
{{HelpAndAbout| |
|||
{{HelpAndAbout1|n=2|s=HOMFLYPT}} |
|||
n = 2 | |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
n1 = 3 | |
|||
{{HelpAndAbout2|n=3|s=HOMFLYPT}} |
|||
in = <nowiki>HOMFLYPT</nowiki> | |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
{{HelpAndAbout3}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
<!--END--> |
<!--END--> |
||
Thus, for example, here's the HOMFLY-PT polynomial of the knot [[8_1]]: |
Thus, for example, here's the HOMFLY-PT polynomial of the knot [[8_1]]: |
||
<!--$$K = Knot[8, 1];$$--> |
<!--$$K = Knot[8, 1];$$--> |
||
<!--Robot Land, no human edits to "END"--> |
|||
<!--The lines to END were generated by WikiSplice: do not edit; see manual.--> |
|||
{{ |
{{In| |
||
n = 4 | |
|||
<pre style="color: red; border: 0px; padding: 0em"><nowiki>K = Knot[8, 1];</nowiki></pre> |
|||
in = <nowiki>K = Knot[8, 1];</nowiki>}} |
|||
{{In2}} |
|||
<!--END--> |
<!--END--> |
||
<!--$$HOMFLYPT[Knot[8, 1]][a, z]$$--> |
<!--$$HOMFLYPT[Knot[8, 1]][a, z]$$--> |
||
<!--Robot Land, no human edits to "END"--> |
|||
<!--The lines to END were generated by WikiSplice: do not edit; see manual.--> |
|||
{{ |
{{InOut| |
||
n = 5 | |
|||
in = <nowiki>HOMFLYPT[Knot[8, 1]][a, z]</nowiki> | |
|||
{{InOut2|n=5}}<pre style="border: 0px; padding: 0em"><nowiki> -2 4 6 2 2 2 4 2 |
|||
out= <nowiki> -2 4 6 2 2 2 4 2 |
|||
a - a + a - z - a z - a z</nowiki>}} |
|||
{{InOut3}} |
|||
<!--END--> |
<!--END--> |
||
It is well known that HOMFLY-PT polynomial specializes to the Jones polynomial at <math>a=q^{-1}</math> and <math>z=q^{1/2}-q^{-1/2}</math> and to the Conway polynomial at <math>a=1</math>. Indeed, |
It is well known that HOMFLY-PT polynomial specializes to the Jones polynomial at <math>a=q^{-1}</math> and <math>z=q^{1/2}-q^{-1/2}</math> and to the Conway polynomial at <math>a=1</math>. Indeed, |
||
<!--$$ |
<!--$$Expand[HOMFLYPT[K][1/q, Sqrt[q]-1/Sqrt[q]]]$$--> |
||
<!--Robot Land, no human edits to "END"--> |
|||
<!--The lines to END were generated by WikiSplice: do not edit; see manual.--> |
|||
{{ |
{{InOut| |
||
n = 6 | |
|||
in = <nowiki>Expand[HOMFLYPT[K][1/q, Sqrt[q]-1/Sqrt[q]]]</nowiki> | |
|||
{{InOut2|n=6}}<pre style="border: 0px; padding: 0em"><nowiki> -6 -5 -4 2 2 2 2 -6 -5 -4 2 2 2 2 |
|||
out= <nowiki> -6 -5 -4 2 2 2 2 |
|||
2 + q - q + q - -- + -- - - - q + q |
|||
3 2 q |
|||
q q</nowiki>}} |
|||
{{InOut3}} |
|||
<!--END--> |
|||
<!--$$Jones[K][q]$$--> |
|||
<!--Robot Land, no human edits to "END"--> |
|||
{{InOut| |
|||
n = 7 | |
|||
in = <nowiki>Jones[K][q]</nowiki> | |
|||
out= <nowiki> -6 -5 -4 2 2 2 2 |
|||
2 + q - q + q - -- + -- - - - q + q |
|||
3 2 q |
|||
q q</nowiki>}} |
|||
<!--END--> |
<!--END--> |
||
<!--$${HOMFLYPT[K][1, z], Conway[K][z]}$$--> |
<!--$${HOMFLYPT[K][1, z], Conway[K][z]}$$--> |
||
<!--Robot Land, no human edits to "END"--> |
|||
<!--The lines to END were generated by WikiSplice: do not edit; see manual.--> |
|||
{{ |
{{InOut| |
||
n = 8 | |
|||
in = <nowiki>{HOMFLYPT[K][1, z], Conway[K][z]}</nowiki> | |
|||
{{InOut2|n=7}}<pre style="border: 0px; padding: 0em"><nowiki> 2 2 |
|||
out= <nowiki> 2 2 |
|||
{1 - 3 z , 1 - 3 z }</nowiki>}} |
|||
{{InOut3}} |
|||
<!--END--> |
<!--END--> |
||
{{Knot Image Pair|8_1|gif|L5a1|gif}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
<center><math>A_2(L)(q) = (-1)^c(q^2+1+q^{-2})H(L)(q^{-3},\,q-q^{-1})</math>,</center> |
<center><math>A_2(L)(q) = (-1)^c(q^2+1+q^{-2})H(L)(q^{-3},\,q-q^{-1})</math>,</center> |
||
| Line 69: | Line 81: | ||
<!--$$L = Link[5, Alternating, 1];$$--> |
<!--$$L = Link[5, Alternating, 1];$$--> |
||
<!--Robot Land, no human edits to "END"--> |
|||
<!--The lines to END were generated by WikiSplice: do not edit; see manual.--> |
|||
{{ |
{{In| |
||
n = 9 | |
|||
in = <nowiki>L = Link[5, Alternating, 1];</nowiki>}} |
|||
{{In2}} |
|||
<!--END--> |
<!--END--> |
||
| Line 79: | Line 91: | ||
A2Invariant[L][q] |
A2Invariant[L][q] |
||
}]$$--> |
}]$$--> |
||
<!--Robot Land, no human edits to "END"--> |
|||
<!--The lines to END were generated by WikiSplice: do not edit; see manual.--> |
|||
{{ |
{{InOut| |
||
n = 10 | |
|||
<pre style="color: red; border: 0px; padding: 0em"><nowiki>Simplify[{ |
|||
in = <nowiki>Simplify[{ |
|||
(-1)^(Length[Skeleton[L]]-1)(q^2+1+1/q^2)HOMFLYPT[L][1/q^3, q-1/q], |
(-1)^(Length[Skeleton[L]]-1)(q^2+1+1/q^2)HOMFLYPT[L][1/q^3, q-1/q], |
||
A2Invariant[L][q] |
A2Invariant[L][q] |
||
}]</nowiki> |
}]</nowiki> | |
||
out= <nowiki> -12 -8 -6 2 -2 2 4 6 |
|||
{2 - q + q + q + -- + q + q + q + q , |
{2 - q + q + q + -- + q + q + q + q , |
||
4 |
|||
q |
q |
||
{{InOut3}} |
|||
-12 -8 -6 2 -2 2 4 6 |
|||
2 - q + q + q + -- + q + q + q + q } |
|||
4 |
|||
q</nowiki>}} |
|||
<!--END--> |
<!--END--> |
||
====Other Software to Compute the HOMFLY-PT Polynomial==== |
|||
A C-based program running under windows by M. Ochiai can compute the HOMFLY-PT polynomial of certain knots and links with up to hundreds of crossings using "base tangle decompositions". His program, bTd, is available at [http://amadeus.ics.nara-wu.ac.jp/~ochiai/freesoft.html]. |
|||
====References==== |
|||
{{note|HOMFLY}} J. Hoste, A. Ocneanu, K. Millett, P. Freyd, W. B. R. Lickorish and D. Yetter, ''A new polynomial invariant of knots and links'', Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. '''12''' (1985) 239-246. |
{{note|HOMFLY}} J. Hoste, A. Ocneanu, K. Millett, P. Freyd, W. B. R. Lickorish and D. Yetter, ''A new polynomial invariant of knots and links'', Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. '''12''' (1985) 239-246. |
||
{{note|PT}} J. Przytycki and P. Traczyk, |
{{note|PT}} J. Przytycki and P. Traczyk, ''Conway Algebras and Skein Equivalence of Links'', Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. '''100''' (1987) 744-748. |
||
Latest revision as of 19:56, 8 August 2013
The HOMFLY-PT polynomial (see [HOMFLY] and [PT]) of a knot or link is defined by the skein relation
and by the initial condition =1.
KnotTheory` knows about the HOMFLY-PT polynomial:
(For In[1] see Setup)
|
| ||||||||
Thus, for example, here's the HOMFLY-PT polynomial of the knot 8_1:
In[4]:=
|
K = Knot[8, 1];
|
In[5]:=
|
HOMFLYPT[Knot[8, 1]][a, z]
|
Out[5]=
|
-2 4 6 2 2 2 4 2
a - a + a - z - a z - a z
|
It is well known that HOMFLY-PT polynomial specializes to the Jones polynomial at and and to the Conway polynomial at . Indeed,
In[6]:=
|
Expand[HOMFLYPT[K][1/q, Sqrt[q]-1/Sqrt[q]]]
|
Out[6]=
|
-6 -5 -4 2 2 2 2
2 + q - q + q - -- + -- - - - q + q
3 2 q
q q
|
In[7]:=
|
Jones[K][q]
|
Out[7]=
|
-6 -5 -4 2 2 2 2
2 + q - q + q - -- + -- - - - q + q
3 2 q
q q
|
In[8]:=
|
{HOMFLYPT[K][1, z], Conway[K][z]}
|
Out[8]=
|
2 2
{1 - 3 z , 1 - 3 z }
|
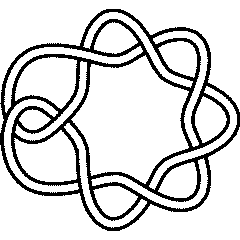 8_1 |
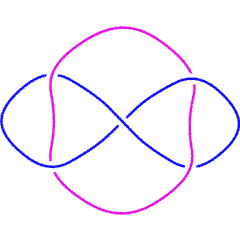 L5a1 |
In our parametrization of the link invariant, it satisfies
where is some knot or link and where is the number of components of . Let us verify this fact for the Whitehead link, L5a1:
In[9]:=
|
L = Link[5, Alternating, 1];
|
In[10]:=
|
Simplify[{
(-1)^(Length[Skeleton[L]]-1)(q^2+1+1/q^2)HOMFLYPT[L][1/q^3, q-1/q],
A2Invariant[L][q]
}]
|
Out[10]=
|
-12 -8 -6 2 -2 2 4 6
{2 - q + q + q + -- + q + q + q + q ,
4
q
-12 -8 -6 2 -2 2 4 6
2 - q + q + q + -- + q + q + q + q }
4
q
|
Other Software to Compute the HOMFLY-PT Polynomial
A C-based program running under windows by M. Ochiai can compute the HOMFLY-PT polynomial of certain knots and links with up to hundreds of crossings using "base tangle decompositions". His program, bTd, is available at [1].
References
[HOMFLY] ^ J. Hoste, A. Ocneanu, K. Millett, P. Freyd, W. B. R. Lickorish and D. Yetter, A new polynomial invariant of knots and links, Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 12 (1985) 239-246.
[PT] ^ J. Przytycki and P. Traczyk, Conway Algebras and Skein Equivalence of Links, Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 100 (1987) 744-748.








