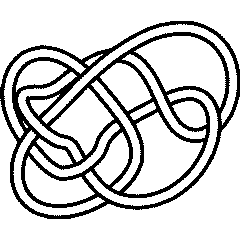
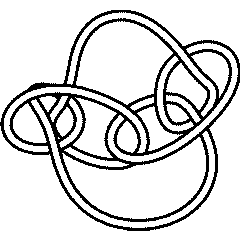10 137: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- --> |
<!-- --> |
||
<!-- --> |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
<!-- --> |
|||
<!-- provide an anchor so we can return to the top of the page --> |
<!-- provide an anchor so we can return to the top of the page --> |
||
<span id="top"></span> |
<span id="top"></span> |
||
<!-- --> |
|||
<!-- this relies on transclusion for next and previous links --> |
<!-- this relies on transclusion for next and previous links --> |
||
{{Knot Navigation Links|ext=gif}} |
{{Knot Navigation Links|ext=gif}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{| align=left |
|||
|- valign=top |
|||
|[[Image:{{PAGENAME}}.gif]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|{{:{{PAGENAME}} Quick Notes}} |
|||
|} |
|||
<br style="clear:both" /> |
<br style="clear:both" /> |
||
| Line 24: | Line 21: | ||
{{Vassiliev Invariants}} |
{{Vassiliev Invariants}} |
||
{{Khovanov Homology|table=<table border=1> |
|||
The coefficients of the monomials <math>t^rq^j</math> are shown, along with their alternating sums <math>\chi</math> (fixed <math>j</math>, alternation over <math>r</math>). The squares with <font class=HLYellow>yellow</font> highlighting are those on the "critical diagonals", where <math>j-2r=s+1</math> or <math>j-2r=s+1</math>, where <math>s=</math>{{Data:{{PAGENAME}}/Signature}} is the signature of {{PAGENAME}}. Nonzero entries off the critical diagonals (if any exist) are highlighted in <font class=HLRed>red</font>. |
|||
<center><table border=1> |
|||
<tr align=center> |
<tr align=center> |
||
<td width=15.3846%><table cellpadding=0 cellspacing=0> |
<td width=15.3846%><table cellpadding=0 cellspacing=0> |
||
| Line 46: | Line 39: | ||
<tr align=center><td>-11</td><td bgcolor=yellow> </td><td bgcolor=yellow>1</td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td>-1</td></tr> |
<tr align=center><td>-11</td><td bgcolor=yellow> </td><td bgcolor=yellow>1</td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td>-1</td></tr> |
||
<tr align=center><td>-13</td><td bgcolor=yellow>1</td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td>1</td></tr> |
<tr align=center><td>-13</td><td bgcolor=yellow>1</td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td>1</td></tr> |
||
</table> |
</table>}} |
||
{{Computer Talk Header}} |
{{Computer Talk Header}} |
||
| Line 125: | Line 117: | ||
q t q t q t</nowiki></pre></td></tr> |
q t q t q t</nowiki></pre></td></tr> |
||
</table> |
</table> |
||
[[Category:Knot Page]] |
|||
Revision as of 19:15, 28 August 2005
|
|
|
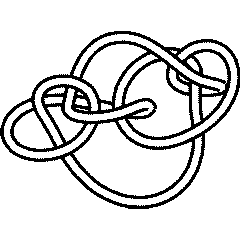
|
Visit 10 137's page at the Knot Server (KnotPlot driven, includes 3D interactive images!)
Visit 10 137's page at Knotilus! Visit 10 137's page at the original Knot Atlas! |
10 137 Further Notes and Views
Knot presentations
| Planar diagram presentation | X1425 X5,10,6,11 X3948 X9,3,10,2 X16,12,17,11 X14,7,15,8 X6,15,7,16 X20,18,1,17 X18,13,19,14 X12,19,13,20 |
| Gauss code | -1, 4, -3, 1, -2, -7, 6, 3, -4, 2, 5, -10, 9, -6, 7, -5, 8, -9, 10, -8 |
| Dowker-Thistlethwaite code | 4 8 10 -14 2 -16 -18 -6 -20 -12 |
| Conway Notation | [22,211,2-] |
Three dimensional invariants
|
Four dimensional invariants
|
Polynomial invariants
| Alexander polynomial | [math]\displaystyle{ t^2-6 t+11-6 t^{-1} + t^{-2} }[/math] |
| Conway polynomial | [math]\displaystyle{ z^4-2 z^2+1 }[/math] |
| 2nd Alexander ideal (db, data sources) | [math]\displaystyle{ \{1\} }[/math] |
| Determinant and Signature | { 25, 0 } |
| Jones polynomial | [math]\displaystyle{ q^2-2 q+4-4 q^{-1} +4 q^{-2} -4 q^{-3} +3 q^{-4} -2 q^{-5} + q^{-6} }[/math] |
| HOMFLY-PT polynomial (db, data sources) | [math]\displaystyle{ a^6-2 z^2 a^4-2 a^4+z^4 a^2+2 z^2 a^2+2 a^2-2 z^2-1+ a^{-2} }[/math] |
| Kauffman polynomial (db, data sources) | [math]\displaystyle{ a^4 z^8+a^2 z^8+2 a^5 z^7+4 a^3 z^7+2 a z^7+a^6 z^6-a^4 z^6-a^2 z^6+z^6-8 a^5 z^5-15 a^3 z^5-7 a z^5-4 a^6 z^4-7 a^4 z^4-5 a^2 z^4-2 z^4+8 a^5 z^3+15 a^3 z^3+9 a z^3+2 z^3 a^{-1} +4 a^6 z^2+8 a^4 z^2+7 a^2 z^2+z^2 a^{-2} +4 z^2-3 a^5 z-5 a^3 z-3 a z-z a^{-1} -a^6-2 a^4-2 a^2- a^{-2} -1 }[/math] |
| The A2 invariant | [math]\displaystyle{ q^{20}+q^{18}-q^{16}-q^{12}-q^{10}+q^8+q^4+ q^{-2} - q^{-4} + q^{-6} + q^{-8} }[/math] |
| The G2 invariant | [math]\displaystyle{ q^{94}-q^{92}+3 q^{90}-4 q^{88}+3 q^{86}-q^{84}-4 q^{82}+10 q^{80}-10 q^{78}+10 q^{76}-4 q^{74}-4 q^{72}+11 q^{70}-12 q^{68}+8 q^{66}-q^{64}-6 q^{62}+8 q^{60}-6 q^{58}-2 q^{56}+9 q^{54}-13 q^{52}+10 q^{50}-5 q^{48}-6 q^{46}+12 q^{44}-15 q^{42}+13 q^{40}-9 q^{38}+3 q^{36}+5 q^{34}-9 q^{32}+11 q^{30}-9 q^{28}+5 q^{26}+3 q^{24}-6 q^{22}+6 q^{20}-2 q^{18}-3 q^{16}+10 q^{14}-11 q^{12}+7 q^{10}+q^8-10 q^6+14 q^4-13 q^2+7+ q^{-2} -7 q^{-4} +7 q^{-6} -5 q^{-8} +3 q^{-10} + q^{-12} -2 q^{-14} + q^{-16} -2 q^{-20} +3 q^{-22} +2 q^{-28} - q^{-30} + q^{-32} + q^{-38} }[/math] |
A1 Invariants.
| Weight | Invariant |
|---|---|
| 1 | [math]\displaystyle{ q^{13}-q^{11}+q^9-q^7+2 q^{-1} - q^{-3} + q^{-5} }[/math] |
| 2 | [math]\displaystyle{ q^{38}-q^{36}-2 q^{34}+3 q^{32}+q^{30}-4 q^{28}+q^{26}+3 q^{24}-2 q^{22}-2 q^{20}+3 q^{18}+q^{16}-3 q^{14}+2 q^{12}+2 q^{10}-3 q^8-q^6+3 q^4-3+3 q^{-2} +2 q^{-4} -3 q^{-6} +2 q^{-10} }[/math] |
| 3 | [math]\displaystyle{ q^{75}-q^{73}-2 q^{71}+4 q^{67}+3 q^{65}-5 q^{63}-6 q^{61}+2 q^{59}+8 q^{57}+3 q^{55}-7 q^{53}-7 q^{51}+2 q^{49}+10 q^{47}+5 q^{45}-10 q^{43}-10 q^{41}+5 q^{39}+14 q^{37}-2 q^{35}-15 q^{33}-q^{31}+14 q^{29}+4 q^{27}-12 q^{25}-4 q^{23}+11 q^{21}+5 q^{19}-10 q^{17}-5 q^{15}+6 q^{13}+7 q^{11}-3 q^9-8 q^7-4 q^5+10 q^3+11 q-5 q^{-1} -15 q^{-3} +18 q^{-7} +3 q^{-9} -14 q^{-11} -7 q^{-13} +9 q^{-15} +8 q^{-17} -4 q^{-19} -5 q^{-21} + q^{-23} +2 q^{-25} + q^{-27} - q^{-29} }[/math] |
A2 Invariants.
| Weight | Invariant |
|---|---|
| 1,0 | [math]\displaystyle{ q^{20}+q^{18}-q^{16}-q^{12}-q^{10}+q^8+q^4+ q^{-2} - q^{-4} + q^{-6} + q^{-8} }[/math] |
| 2,0 | [math]\displaystyle{ q^{52}+q^{50}-3 q^{46}-2 q^{44}+q^{42}+2 q^{40}-q^{36}+2 q^{34}+2 q^{32}-3 q^{28}-q^{26}+q^{22}+q^{18}+3 q^{16}-2 q^{10}-q^8+q^4-q^2-1+2 q^{-2} +3 q^{-4} -3 q^{-8} + q^{-10} +2 q^{-12} + q^{-20} }[/math] |
A3 Invariants.
| Weight | Invariant |
|---|---|
| 0,1,0 | [math]\displaystyle{ q^{40}-q^{38}+q^{36}+q^{34}-2 q^{32}+q^{30}-q^{28}-q^{26}+2 q^{24}+2 q^{18}-q^{14}-q^{10}-q^6+2 q^2-1+ q^{-2} +2 q^{-4} -2 q^{-6} + q^{-8} +2 q^{-10} + q^{-16} }[/math] |
| 1,0,0 | [math]\displaystyle{ q^{27}+q^{25}+q^{23}-q^{21}-2 q^{17}-q^{15}-q^{13}+q^{11}+q^9+q^7+q^5- q^{-1} + q^{-3} - q^{-5} + q^{-7} + q^{-9} + q^{-11} }[/math] |
B2 Invariants.
| Weight | Invariant |
|---|---|
| 0,1 | [math]\displaystyle{ q^{40}-q^{38}+3 q^{36}-3 q^{34}+4 q^{32}-3 q^{30}+3 q^{28}-3 q^{26}-4 q^{20}+4 q^{18}-6 q^{16}+7 q^{14}-6 q^{12}+7 q^{10}-4 q^8+3 q^6+1-3 q^{-2} +4 q^{-4} -4 q^{-6} +3 q^{-8} -2 q^{-10} +2 q^{-12} + q^{-16} }[/math] |
| 1,0 | [math]\displaystyle{ q^{66}-q^{62}-q^{60}+2 q^{58}+2 q^{56}-2 q^{54}-3 q^{52}+q^{50}+3 q^{48}-4 q^{44}-2 q^{42}+4 q^{40}+3 q^{38}-q^{36}-3 q^{34}+q^{32}+3 q^{30}+q^{28}-2 q^{26}-q^{24}+2 q^{22}+q^{20}-2 q^{18}-3 q^{16}+q^{14}+3 q^{12}-q^{10}-4 q^8+3 q^4+2 q^2-2-2 q^{-2} +2 q^{-4} +4 q^{-6} - q^{-8} -3 q^{-10} +2 q^{-14} +2 q^{-16} - q^{-20} + q^{-26} }[/math] |
G2 Invariants.
| Weight | Invariant |
|---|---|
| 1,0 | [math]\displaystyle{ q^{94}-q^{92}+3 q^{90}-4 q^{88}+3 q^{86}-q^{84}-4 q^{82}+10 q^{80}-10 q^{78}+10 q^{76}-4 q^{74}-4 q^{72}+11 q^{70}-12 q^{68}+8 q^{66}-q^{64}-6 q^{62}+8 q^{60}-6 q^{58}-2 q^{56}+9 q^{54}-13 q^{52}+10 q^{50}-5 q^{48}-6 q^{46}+12 q^{44}-15 q^{42}+13 q^{40}-9 q^{38}+3 q^{36}+5 q^{34}-9 q^{32}+11 q^{30}-9 q^{28}+5 q^{26}+3 q^{24}-6 q^{22}+6 q^{20}-2 q^{18}-3 q^{16}+10 q^{14}-11 q^{12}+7 q^{10}+q^8-10 q^6+14 q^4-13 q^2+7+ q^{-2} -7 q^{-4} +7 q^{-6} -5 q^{-8} +3 q^{-10} + q^{-12} -2 q^{-14} + q^{-16} -2 q^{-20} +3 q^{-22} +2 q^{-28} - q^{-30} + q^{-32} + q^{-38} }[/math] |
.
KnotTheory`, as shown in the (simulated) Mathematica session below. Your input (in red) is realistic; all else should have the same content as in a real mathematica session, but with different formatting. This Mathematica session is also available (albeit only for the knot 5_2) as the notebook PolynomialInvariantsSession.nb.
(The path below may be different on your system, and possibly also the KnotTheory` date)
In[1]:=
|
AppendTo[$Path, "C:/drorbn/projects/KAtlas/"];
<< KnotTheory`
|
Loading KnotTheory` version of August 31, 2006, 11:25:27.5625.
|
In[3]:=
|
K = Knot["10 137"];
|
In[4]:=
|
Alexander[K][t]
|
KnotTheory::loading: Loading precomputed data in PD4Knots`.
|
Out[4]=
|
[math]\displaystyle{ t^2-6 t+11-6 t^{-1} + t^{-2} }[/math] |
In[5]:=
|
Conway[K][z]
|
Out[5]=
|
[math]\displaystyle{ z^4-2 z^2+1 }[/math] |
In[6]:=
|
Alexander[K, 2][t]
|
KnotTheory::credits: The program Alexander[K, r] to compute Alexander ideals was written by Jana Archibald at the University of Toronto in the summer of 2005.
|
Out[6]=
|
[math]\displaystyle{ \{1\} }[/math] |
In[7]:=
|
{KnotDet[K], KnotSignature[K]}
|
Out[7]=
|
{ 25, 0 } |
In[8]:=
|
Jones[K][q]
|
KnotTheory::loading: Loading precomputed data in Jones4Knots`.
|
Out[8]=
|
[math]\displaystyle{ q^2-2 q+4-4 q^{-1} +4 q^{-2} -4 q^{-3} +3 q^{-4} -2 q^{-5} + q^{-6} }[/math] |
In[9]:=
|
HOMFLYPT[K][a, z]
|
KnotTheory::credits: The HOMFLYPT program was written by Scott Morrison.
|
Out[9]=
|
[math]\displaystyle{ a^6-2 z^2 a^4-2 a^4+z^4 a^2+2 z^2 a^2+2 a^2-2 z^2-1+ a^{-2} }[/math] |
In[10]:=
|
Kauffman[K][a, z]
|
KnotTheory::loading: Loading precomputed data in Kauffman4Knots`.
|
Out[10]=
|
[math]\displaystyle{ a^4 z^8+a^2 z^8+2 a^5 z^7+4 a^3 z^7+2 a z^7+a^6 z^6-a^4 z^6-a^2 z^6+z^6-8 a^5 z^5-15 a^3 z^5-7 a z^5-4 a^6 z^4-7 a^4 z^4-5 a^2 z^4-2 z^4+8 a^5 z^3+15 a^3 z^3+9 a z^3+2 z^3 a^{-1} +4 a^6 z^2+8 a^4 z^2+7 a^2 z^2+z^2 a^{-2} +4 z^2-3 a^5 z-5 a^3 z-3 a z-z a^{-1} -a^6-2 a^4-2 a^2- a^{-2} -1 }[/math] |
Vassiliev invariants
| V2 and V3: | (-2, 2) |
| V2,1 through V6,9: |
|
V2,1 through V6,9 were provided by Petr Dunin-Barkowski <barkovs@itep.ru>, Andrey Smirnov <asmirnov@itep.ru>, and Alexei Sleptsov <sleptsov@itep.ru> and uploaded on October 2010 by User:Drorbn. Note that they are normalized differently than V2 and V3.
Khovanov Homology
| The coefficients of the monomials [math]\displaystyle{ t^rq^j }[/math] are shown, along with their alternating sums [math]\displaystyle{ \chi }[/math] (fixed [math]\displaystyle{ j }[/math], alternation over [math]\displaystyle{ r }[/math]). The squares with yellow highlighting are those on the "critical diagonals", where [math]\displaystyle{ j-2r=s+1 }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ j-2r=s-1 }[/math], where [math]\displaystyle{ s= }[/math]0 is the signature of 10 137. Nonzero entries off the critical diagonals (if any exist) are highlighted in red. |
|
| Integral Khovanov Homology
(db, data source) |
|
Computer Talk
Much of the above data can be recomputed by Mathematica using the package KnotTheory`. See A Sample KnotTheory` Session.
[math]\displaystyle{ \textrm{Include}(\textrm{ColouredJonesM.mhtml}) }[/math]
In[1]:= |
<< KnotTheory` |
Loading KnotTheory` (version of August 17, 2005, 14:44:34)... | |
In[2]:= | Crossings[Knot[10, 137]] |
Out[2]= | 10 |
In[3]:= | PD[Knot[10, 137]] |
Out[3]= | PD[X[1, 4, 2, 5], X[5, 10, 6, 11], X[3, 9, 4, 8], X[9, 3, 10, 2],X[16, 12, 17, 11], X[14, 7, 15, 8], X[6, 15, 7, 16],X[20, 18, 1, 17], X[18, 13, 19, 14], X[12, 19, 13, 20]] |
In[4]:= | GaussCode[Knot[10, 137]] |
Out[4]= | GaussCode[-1, 4, -3, 1, -2, -7, 6, 3, -4, 2, 5, -10, 9, -6, 7, -5, 8, -9, 10, -8] |
In[5]:= | BR[Knot[10, 137]] |
Out[5]= | BR[5, {-1, 2, -1, 2, -3, -2, -2, 4, -3, 4}] |
In[6]:= | alex = Alexander[Knot[10, 137]][t] |
Out[6]= | -2 6 2 |
In[7]:= | Conway[Knot[10, 137]][z] |
Out[7]= | 2 4 1 - 2 z + z |
In[8]:= | Select[AllKnots[], (alex === Alexander[#][t])&] |
Out[8]= | {Knot[10, 137]} |
In[9]:= | {KnotDet[Knot[10, 137]], KnotSignature[Knot[10, 137]]} |
Out[9]= | {25, 0} |
In[10]:= | J=Jones[Knot[10, 137]][q] |
Out[10]= | -6 2 3 4 4 4 2 |
In[11]:= | Select[AllKnots[], (J === Jones[#][q] || (J /. q-> 1/q) === Jones[#][q])&] |
Out[11]= | {Knot[10, 137], Knot[10, 155], Knot[11, NonAlternating, 37]} |
In[12]:= | A2Invariant[Knot[10, 137]][q] |
Out[12]= | -20 -18 -16 -12 -10 -8 -4 2 4 6 8 q + q - q - q - q + q + q + q - q + q + q |
In[13]:= | Kauffman[Knot[10, 137]][a, z] |
Out[13]= | 2-2 2 4 6 z 3 5 2 z |
In[14]:= | {Vassiliev[2][Knot[10, 137]], Vassiliev[3][Knot[10, 137]]} |
Out[14]= | {0, 2} |
In[15]:= | Kh[Knot[10, 137]][q, t] |
Out[15]= | 2 1 1 1 2 1 2 2 |