Identifying Knots within a List: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Manual TOC Sidebar}} |
{{Manual TOC Sidebar}} |
||
IdentifyWithin[L,H] returns those elements from the list of knots H, whose invariant matches that of the knot L. It can also recognize mirrors and connected sums of the knots in the list. Its options include turning off (on) the search for connected sums with ConnectedSum->False (True) and choosing the invariants to be used in identification by selecting, for example, Invariants->{Jones[#][q]&, HOMFLYPT[#][a,z]&}. |
<code>IdentifyWithin[L,H]</code> returns those elements from the list of knots <math>H</math>, whose invariant matches that of the knot <math>L</math>. It can also recognize mirrors and connected sums of the knots in the list. Its options include turning off (on) the search for connected sums with <code>ConnectedSum->False (True)</code> and choosing the invariants to be used in identification by selecting, for example, <code>Invariants->{Jones[#][q]&, HOMFLYPT[#][a,z]&}</code>. |
||
IdentifyWithin can be used together with [[Prime Links with a Non-Prime Component|SubLink]] to determine the components of a link. For the second component of link [[L11n150]], for instance, we get: |
<code>IdentifyWithin</code> can be used together with [[Prime Links with a Non-Prime Component|<code>SubLink</code>]] to determine the components of a link. For the second component of link [[L11n150]], for instance, we get: |
||
{{Startup Note}} |
{{Startup Note}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
<!--$$Options[IdentifyWithin] = { |
<!--$$Options[IdentifyWithin] = { |
||
| Line 170: | Line 156: | ||
];</nowiki>}} |
];</nowiki>}} |
||
<!--END--> |
<!--END--> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
Revision as of 10:23, 8 November 2007
IdentifyWithin[L,H] returns those elements from the list of knots , whose invariant matches that of the knot . It can also recognize mirrors and connected sums of the knots in the list. Its options include turning off (on) the search for connected sums with ConnectedSum->False (True) and choosing the invariants to be used in identification by selecting, for example, Invariants->{Jones[#][q]&, HOMFLYPT[#][a,z]&}.
IdentifyWithin can be used together with SubLink to determine the components of a link. For the second component of link L11n150, for instance, we get:
(For In[1] see Setup)
In[3]:=
|
Options[IdentifyWithin] = {
Invariants -> {Jones[#][q] &, HOMFLYPT[#][a, z] &,
Kauffman[#][a, z] &},
ConnectedSum -> "True"};
IdentifyWithin[L_, H_List, opts___Rule] :=
Module[
{div, j = 1, l, i = 1, u, mu, t, mt, out = {}, out1 = {}, nk, mnk,
mnk1, p, mp, m, p1,
invariants = (Invariants /. {opts} /. Options[IdentifyWithin]),
connectedsum = (ConnectedSum /. {opts} /.
Options[IdentifyWithin])},
NormalizeP[poly_] := Module[{t1, i1},
(For[i1 = 1 ; t1 := FactorList[poly],
i1 <= Length[Variables[poly]], i1++,
t1 =
DeleteCases[t1, {Variables[poly][[i1]], _Integer} | {1, 1}]];
Times @@ Power @@@ t1 )];
l := Length[invariants];
u[0] = mu[0] = H;
While[i <= l && ! Length[out] === 1,
t[i] = invariants[[i]][L];
mt[i] = invariants[[i]][Mirror[L]];
u[i] = Select[u[i - 1], t[i] == invariants[[i]][#] &];
mu[i] = Select[mu[i - 1], mt[i] == invariants[[i]][#] &];
out = Flatten[{u[i], Mirror /@ mu[i]}];
i++];
Which[
Length[out] >= 2, DeleteCases[out, Mirror[Knot[0, 1]]],
Length[out] == 1,
out = If[u[i - 1] != {}, u[i - 1], Mirror /@ mu[i - 1]],
connectedsum === "True", i = 1; nk[0] = mnk[0] = H;
While[Length[out1] != 1 && i <= l,
p[i] = NormalizeP[t[i]];
mp[i] = NormalizeP[mt[i]];
nk[i] =
Select[nk[i - 1], (p1 = NormalizeP[invariants[[i]][#]]; z = 3;
PolynomialRemainder[p[i], p1, Variables[p[i]][[1]]] ===
0 ) &];
mnk[i] =
Select[mnk[i - 1], (p1 = NormalizeP[invariants[[i]][#]]; z = 3;
PolynomialRemainder[mp[i], p1, Variables[p[i]][[1]]] ===
0 ) &];
Clear[z];
mnk1[i] = Mirror /@ mnk[i];
div = Flatten[{nk[i], mnk1[i]}];
div = DeleteCases[div, Knot[0, 1] | Mirror[Knot[0, 1]]];
If[div == {}, out1 = {},
For[m = 1;
W[0] =
CS[0] = Select[
Flatten /@ Flatten[Outer[List, div, div, 1], 1], OrderedQ],
Length[W[m - 1][[1]]] < 4, m++,
W[m] = Select[
Flatten /@ Flatten[Outer[List, div, W[m - 1], 1], 1],
OrderedQ];
CS[m] = Flatten[{CS[m - 1], W[m]}, 1];
];
out1 =
Select[CS[m - 1],
Expand[Times @@ invariants[[i]] /@ #] == t[i] &];
];
i++];
If[out1 == {}, {}, ConnectedSum @@@ out1], True, {}
]
];
|
In[2]:=
|
IdentifyWithin[SubLink[Link["L11n150"], 2], AllKnots[]]
|
Out[2]=
|
{Knot[5, 2]}
|
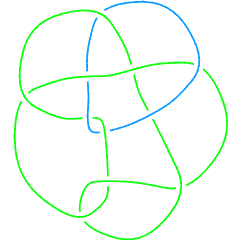 L11n150 |
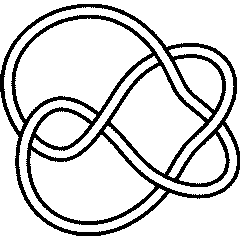 5_2 |
Unfortunately, the program does not provide absolute identification when all the used invariants cannot distinguish between two or more different knots. In that case, a list of possible candidates for is returned.

