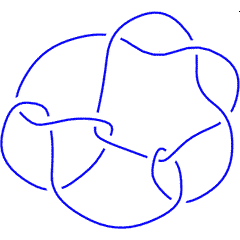
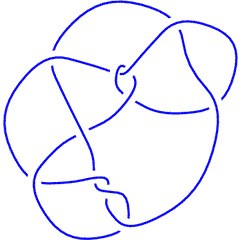
K11n58
|
|
|
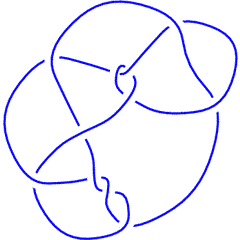 (Knotscape image) |
See the full Hoste-Thistlethwaite Table of 11 Crossing Knots. |
Knot presentations
| Planar diagram presentation | X4251 X8493 X14,5,15,6 X2837 X9,17,10,16 X11,18,12,19 X13,20,14,21 X6,15,7,16 X17,1,18,22 X19,12,20,13 X21,10,22,11 |
| Gauss code | 1, -4, 2, -1, 3, -8, 4, -2, -5, 11, -6, 10, -7, -3, 8, 5, -9, 6, -10, 7, -11, 9 |
| Dowker-Thistlethwaite code | 4 8 14 2 -16 -18 -20 6 -22 -12 -10 |
| A Braid Representative | |||||
| A Morse Link Presentation | 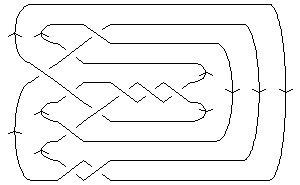
|
Three dimensional invariants
|
Four dimensional invariants
|
Polynomial invariants
| Alexander polynomial | [math]\displaystyle{ t^3-4 t^2+8 t-9+8 t^{-1} -4 t^{-2} + t^{-3} }[/math] |
| Conway polynomial | [math]\displaystyle{ z^6+2 z^4+z^2+1 }[/math] |
| 2nd Alexander ideal (db, data sources) | [math]\displaystyle{ \{1\} }[/math] |
| Determinant and Signature | { 35, -2 } |
| Jones polynomial | [math]\displaystyle{ -q^4+2 q^3-3 q^2+5 q-5+6 q^{-1} -5 q^{-2} +4 q^{-3} -3 q^{-4} + q^{-5} }[/math] |
| HOMFLY-PT polynomial (db, data sources) | [math]\displaystyle{ z^6-2 a^2 z^4-z^4 a^{-2} +5 z^4+a^4 z^2-6 a^2 z^2-3 z^2 a^{-2} +9 z^2+a^4-4 a^2-2 a^{-2} +6 }[/math] |
| Kauffman polynomial (db, data sources) | [math]\displaystyle{ a z^9+z^9 a^{-1} +2 a^2 z^8+2 z^8 a^{-2} +4 z^8+2 a^3 z^7-a z^7-2 z^7 a^{-1} +z^7 a^{-3} +a^4 z^6-6 a^2 z^6-10 z^6 a^{-2} -17 z^6-5 a^3 z^5-5 a z^5-5 z^5 a^{-1} -5 z^5 a^{-3} +8 a^2 z^4+15 z^4 a^{-2} +23 z^4+3 a^5 z^3+6 a^3 z^3+6 a z^3+10 z^3 a^{-1} +7 z^3 a^{-3} +a^6 z^2-10 a^2 z^2-8 z^2 a^{-2} -17 z^2-a^5 z-3 a^3 z-4 a z-4 z a^{-1} -2 z a^{-3} +a^4+4 a^2+2 a^{-2} +6 }[/math] |
| The A2 invariant | [math]\displaystyle{ q^{16}-q^{12}-2 q^8+q^2+3+ q^{-2} +2 q^{-4} - q^{-8} - q^{-12} }[/math] |
| The G2 invariant | Data:K11n58/QuantumInvariant/G2/1,0 |
KnotTheory`, as shown in the (simulated) Mathematica session below. Your input (in red) is realistic; all else should have the same content as in a real mathematica session, but with different formatting. This Mathematica session is also available (albeit only for the knot 5_2) as the notebook PolynomialInvariantsSession.nb.
(The path below may be different on your system, and possibly also the KnotTheory` date)
In[1]:=
|
AppendTo[$Path, "C:/drorbn/projects/KAtlas/"];
<< KnotTheory`
|
Loading KnotTheory` version of August 31, 2006, 11:25:27.5625.
|
In[3]:=
|
K = Knot["K11n58"];
|
In[4]:=
|
Alexander[K][t]
|
KnotTheory::loading: Loading precomputed data in PD4Knots`.
|
Out[4]=
|
[math]\displaystyle{ t^3-4 t^2+8 t-9+8 t^{-1} -4 t^{-2} + t^{-3} }[/math] |
In[5]:=
|
Conway[K][z]
|
Out[5]=
|
[math]\displaystyle{ z^6+2 z^4+z^2+1 }[/math] |
In[6]:=
|
Alexander[K, 2][t]
|
KnotTheory::credits: The program Alexander[K, r] to compute Alexander ideals was written by Jana Archibald at the University of Toronto in the summer of 2005.
|
Out[6]=
|
[math]\displaystyle{ \{1\} }[/math] |
In[7]:=
|
{KnotDet[K], KnotSignature[K]}
|
Out[7]=
|
{ 35, -2 } |
In[8]:=
|
Jones[K][q]
|
KnotTheory::loading: Loading precomputed data in Jones4Knots`.
|
Out[8]=
|
[math]\displaystyle{ -q^4+2 q^3-3 q^2+5 q-5+6 q^{-1} -5 q^{-2} +4 q^{-3} -3 q^{-4} + q^{-5} }[/math] |
In[9]:=
|
HOMFLYPT[K][a, z]
|
KnotTheory::credits: The HOMFLYPT program was written by Scott Morrison.
|
Out[9]=
|
[math]\displaystyle{ z^6-2 a^2 z^4-z^4 a^{-2} +5 z^4+a^4 z^2-6 a^2 z^2-3 z^2 a^{-2} +9 z^2+a^4-4 a^2-2 a^{-2} +6 }[/math] |
In[10]:=
|
Kauffman[K][a, z]
|
KnotTheory::loading: Loading precomputed data in Kauffman4Knots`.
|
Out[10]=
|
[math]\displaystyle{ a z^9+z^9 a^{-1} +2 a^2 z^8+2 z^8 a^{-2} +4 z^8+2 a^3 z^7-a z^7-2 z^7 a^{-1} +z^7 a^{-3} +a^4 z^6-6 a^2 z^6-10 z^6 a^{-2} -17 z^6-5 a^3 z^5-5 a z^5-5 z^5 a^{-1} -5 z^5 a^{-3} +8 a^2 z^4+15 z^4 a^{-2} +23 z^4+3 a^5 z^3+6 a^3 z^3+6 a z^3+10 z^3 a^{-1} +7 z^3 a^{-3} +a^6 z^2-10 a^2 z^2-8 z^2 a^{-2} -17 z^2-a^5 z-3 a^3 z-4 a z-4 z a^{-1} -2 z a^{-3} +a^4+4 a^2+2 a^{-2} +6 }[/math] |
"Similar" Knots (within the Atlas)
Same Alexander/Conway Polynomial: {8_16, 10_156, K11n15, K11n56,}
Same Jones Polynomial (up to mirroring, [math]\displaystyle{ q\leftrightarrow q^{-1} }[/math]): {K11n56,}
KnotTheory`. Your input (in red) is realistic; all else should have the same content as in a real mathematica session, but with different formatting.
(The path below may be different on your system, and possibly also the KnotTheory` date)
In[1]:=
|
AppendTo[$Path, "C:/drorbn/projects/KAtlas/"];
<< KnotTheory`
|
Loading KnotTheory` version of May 31, 2006, 14:15:20.091.
|
In[3]:=
|
K = Knot["K11n58"];
|
In[4]:=
|
{A = Alexander[K][t], J = Jones[K][q]}
|
KnotTheory::loading: Loading precomputed data in PD4Knots`.
|
KnotTheory::loading: Loading precomputed data in Jones4Knots`.
|
Out[4]=
|
{ [math]\displaystyle{ t^3-4 t^2+8 t-9+8 t^{-1} -4 t^{-2} + t^{-3} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ -q^4+2 q^3-3 q^2+5 q-5+6 q^{-1} -5 q^{-2} +4 q^{-3} -3 q^{-4} + q^{-5} }[/math] } |
In[5]:=
|
DeleteCases[Select[AllKnots[], (A === Alexander[#][t]) &], K]
|
KnotTheory::loading: Loading precomputed data in DTCode4KnotsTo11`.
|
KnotTheory::credits: The GaussCode to PD conversion was written by Siddarth Sankaran at the University of Toronto in the summer of 2005.
|
Out[5]=
|
{8_16, 10_156, K11n15, K11n56,} |
In[6]:=
|
DeleteCases[
Select[
AllKnots[],
(J === Jones[#][q] || (J /. q -> 1/q) === Jones[#][q]) &
],
K
]
|
KnotTheory::loading: Loading precomputed data in Jones4Knots11`.
|
Out[6]=
|
{K11n56,} |
Vassiliev invariants
| V2 and V3: | (1, 1) |
| V2,1 through V6,9: |
|
V2,1 through V6,9 were provided by Petr Dunin-Barkowski <barkovs@itep.ru>, Andrey Smirnov <asmirnov@itep.ru>, and Alexei Sleptsov <sleptsov@itep.ru> and uploaded on October 2010 by User:Drorbn. Note that they are normalized differently than V2 and V3.
Khovanov Homology
| The coefficients of the monomials [math]\displaystyle{ t^rq^j }[/math] are shown, along with their alternating sums [math]\displaystyle{ \chi }[/math] (fixed [math]\displaystyle{ j }[/math], alternation over [math]\displaystyle{ r }[/math]). The squares with yellow highlighting are those on the "critical diagonals", where [math]\displaystyle{ j-2r=s+1 }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ j-2r=s-1 }[/math], where [math]\displaystyle{ s= }[/math]-2 is the signature of K11n58. Nonzero entries off the critical diagonals (if any exist) are highlighted in red. |
|
| Integral Khovanov Homology
(db, data source) |
|
Computer Talk
Much of the above data can be recomputed by Mathematica using the package KnotTheory`. See A Sample KnotTheory` Session.
Modifying This Page
| Read me first: Modifying Knot Pages.
See/edit the Hoste-Thistlethwaite Knot Page master template (intermediate). See/edit the Hoste-Thistlethwaite_Splice_Base (expert). Back to the top. |
|